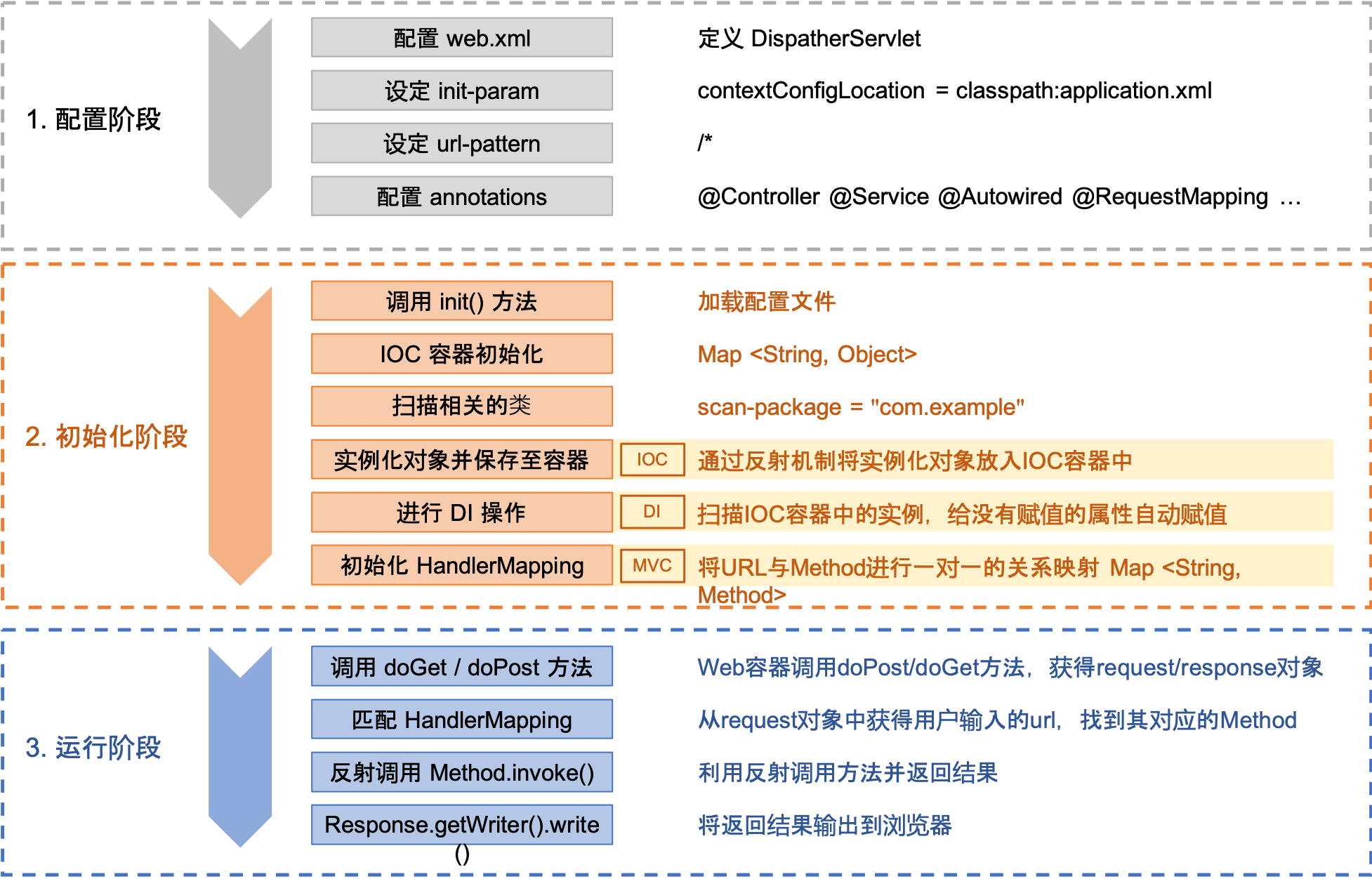
Spring 的运行思路
Spring 的整个启动流程大致可以分为三个阶段:
- 配置阶段
- 初始化阶段
- 运行阶段
梦开始的地方
spring 配置文件
首先,我们准备一个配置文件来模拟 spring-application.xml 中的配置,为了偷懒方便解析,我们就直接写一个 minispring-config.properties 文件:
scanPackage=com.minispring.demo
Servlet 配置文件
大家都知道,所有依赖于 Web 容器的项目都是从读取 web.xml 文件中的配置开始的,这时 Servlet 的起点。我们先配置好 web.xml 中的内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<display-name>MiniSpring Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>minispring-mvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.minispring.framework.MyDispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>minispring-config.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>minispring-mvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
其中 MyDispatcherServlet 是我们自己模拟 Spring 实现的核心功能类。
实现阶段
流程思路
从 Servlet 的配合初始化 init 方法为入口,我们先定义出整个流程的接口方法:
public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final String CONTEXT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "contextConfigLocation";
private static final String CONFIG_SCAN_PACKAGE = "scanPackage";
// 配置文件中的设置
private final Properties contextConfigProperties = new Properties();
// 包路径下扫描的所有类名
private final List<String> clazzes = new ArrayList<>();
// IoC 容器,为了简化暂不考虑 ConcurrentHashMap
private final Map<String, Object> ioc = new HashMap<>();
// URL 与 Method 的对应关系
private final Map<String, Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
// 1. 加载 Servlet 配置文件/从注解加载
String contextConfigLocation = config.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CONFIG_LOCATION);
this.loadContextConfig(contextConfigLocation);
// 2. 获取需要扫描的包路径
String scanPackage = contextConfigProperties.getProperty(CONFIG_SCAN_PACKAGE);
this.scanPackage(scanPackage);
// 3. [IoC] 初始化扫描到的类,并存入 IoC 容器中
this.initClazzInstance();
// 4. [AOP] 通过动态代理生成增强的 AOP 对象
// delegateProxyObjects();
// 5. [DI] 处理依赖注入(Autowired)
this.handleAutowired();
// 6. [MVC] 初始化 URL 与 Method 的 HandlerMapping
this.initHandlerMapping();
// 7. 初始化结束,处理逻辑交还给 Servlet
logger.info("MyDispatcherServlet init done.");
}
}
加载 Servlet 配置文件
// 1. 加载 Servlet 配置文件/从注解加载
private void loadContextConfig(String contextConfigLocation) {
try (InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation)) {
contextConfigProperties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
扫描包
// 2. 获取需要扫描的包路径
private void scanPackage(String scanPackage) {
// 将包名替换为文件路径
String resourcePath = "/" + scanPackage.replace(".", "/");
URL packageURL = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(resourcePath);
if (packageURL == null) {
logger.error("Configured package [{}] is not found", resourcePath);
throw new RuntimeException("Configured package is not found");
}
File rootDir = new File(packageURL.getFile());
for (File dir : rootDir.listFiles()) {
if (dir.isDirectory()) {
this.scanPackage(scanPackage + "." + dir.getName());
} else {
if (!dir.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
continue;
}
String clazzFullName = scanPackage + "." +
dir.getName().replace(".class", "");
clazzes.add(clazzFullName);
}
}
}
初始化类实例与 IoC 容器
// 3. [IoC] 初始化扫描到的类,并存入 IoC 容器中
// 工厂模式的体现
private void initClazzInstance() {
try {
for (String clazzName : clazzes) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(clazzName);
// 存在 @MyController 注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)) {
String beanName = StringUtils.lowercaseInitial(clazz.getSimpleNam());
Object instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
ioc.put(beanName, instance);
} else if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyService.class)) {
// 获取 @MyService 注解中的自定义名
String beanName = clazz.getAnnotation(MyService.class).value();
if (beanName.isEmpty()) {
// 没有自定义的名字,则默认使用小写类名
beanName = StringUtils.lowercaseInitial(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
Object instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 保存实例至 IoC 容器,注意:此处有可能是接口
ioc.put(beanName, instance);
// 判断容器中是否有一个接口有多个实现
for (Class<?> intf : clazz.getInterfaces()) {
if (ioc.containsKey(intf.getName())) {
// 如果存在多个实现类
// TODO: conditional implements
logger.error("Interface {} is already implemented", intfgetName());
throw new RuntimeException("Interface is alreadyimplemented");
}
// 接口类名作为 key
ioc.put(intf.getName(), instance);
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | IllegalAccessException |InstantiationException | NoSuchMethodException | InvocationTargetException e) {
logger.error("Init clazz fail: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
处理依赖注入
// 5. [DI] 处理依赖注入(Autowired)
private void handleAutowired() {
if (ioc.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) {
Class<?> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
// 获取所有 public / protected / private 方法
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {
if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAutowired.class)) {
continue;
}
String beanName = field.getAnnotation(MyAutowired.class).value().trim(;
if (beanName.isEmpty()) {
// 没有自定义类名,默认使用类名注入
beanName = field.getType().getName();
}
// 即使是非 public 方法,但是设置了注解,也需要强制注入
field.setAccessible(true);
// 注意:对于循环引用,需要两次循环处理
// TODO: handle circular reference
try {
Object bean = ioc.get(beanName);
field.set(entry.getValue(), bean);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
logger.error("Set {}.{} fail", clazz.getName(), field.getName());
}
}
}
}
初始化 HandlerMapping
// 6. [MVC] 初始化 URL 与 Method 的 HandlerMapping
// 策略模式的体现
private void initHandlerMapping() {
if (ioc.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) {
Class<?> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)) {
continue;
}
String baseUrl = "";
// 获取类上 @MyRequestMapping 注解的 BaseURL
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)) {
MyRequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMappingclass);
baseUrl = requestMapping.value();
}
// 只遍历 public 方法
for (Method method : clazz.getMethods()) {
// 获取方法上 @MyRequestMapping 注解的 URL
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)) {
String suffixUrl = method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class)value();
// 迷你的解释器模式:拼接 URL 并修正"/"
String url = ("/" + baseUrl + "/" + suffixUrl).replaceAll("/+", "");
handlerMapping.put(url, method);
logger.info("Mapped url {} to method {}", url, method.getName());
}
}
}
}
Servlet 请求分发
public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
// 委派模式,根据 URL 在 HandlerMapping 中找到对应的 Method 并处理请求
this.doDispatch(req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
resp.getWriter().write("500 Internal Error, Exception : " + Arrays.toString(e.getStackTrace()));
logger.error("Write response fail, ", e);
}
}
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
String url = req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = req.getContextPath();
url = url.replace(contextPath, "").replaceAll("/+", "/");
if (!handlerMapping.containsKey(url)) {
resp.getWriter().write("404 Not Found: " + url);
return;
}
// 初始化形参列表
Map<String, String[]> params = req.getParameterMap();
Method method = handlerMapping.get(url);
// 实参列表要根据形参列表才能决定,首先得到形参列表
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Object[] paramValues = new Object[parameterTypes.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
if (parameterType == HttpServletRequest.class) {
paramValues[i] = req;
} else if (parameterType == HttpServletResponse.class) {
paramValues[i] = resp;
} else if (parameterType == String.class) {
// @MyRequestParam 是运行时注解,需要动态获取
Annotation[][] pa = method.getParameterAnnotations();
for (int j = 0; j < pa.length; j++) {
for (Annotation a : pa[i]) {
if (a instanceof MyRequestParam) {
String paramName = ((MyRequestParam) a).value();
if (!paramName.trim().isEmpty()) {
String value = Arrays.toString(params.get(paramName))
.replaceAll("\\[|]", "")
.replaceAll("\\s+", ",");
paramValues[i] = value;
}
}
}
}
}
}
String beanName = StringUtils.lowercaseInitial(method.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName());
// 从 IoC 容器中获取方法,并传入实参列表调用
method.invoke(ioc.get(beanName), paramValues);
}
}
下一步优化
至此,我们已经实现了 MiniSpring 的基本功能,但代码还不够优雅。例如:
- 我们的
HandlerMapping还不能像 SpringMVC 一样支持正则 - URL 的参数也不支持强制类型转换
- 在反射调用前还需要重新获取 beanName
文章评论